AWS Management Console: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know
Ever felt overwhelmed by managing cloud resources? The AWS Management Console is your ultimate gateway to controlling Amazon Web Services with ease, precision, and power. This intuitive web interface puts the entire AWS ecosystem at your fingertips—no command lines required.
What Is the AWS Management Console?

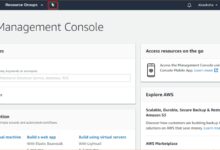
The AWS Management Console is a web-based user interface that allows users to interact with Amazon Web Services (AWS) using a graphical dashboard. Instead of relying solely on command-line tools or APIs, the console provides a visual way to configure, monitor, and manage AWS resources across various services such as EC2, S3, Lambda, RDS, and more.
Core Purpose and Functionality
At its heart, the AWS Management Console simplifies cloud infrastructure management. It enables developers, system administrators, and business users to launch instances, store data, set up networking, and manage security settings—all through a point-and-click environment. This makes it ideal for beginners and experts alike who want a real-time view of their cloud environment.
- Provides centralized access to over 200 AWS services
- Supports multi-account and multi-region navigation
- Offers real-time monitoring and alerts via integrated dashboards
According to AWS’s official documentation, the console is designed to be consistent across services, ensuring a predictable user experience whether you’re configuring a VPC or deploying a machine learning model with SageMaker (AWS Console Overview).
How It Differs From CLI and SDKs
While the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) and Software Development Kits (SDKs) offer programmatic control, the AWS Management Console excels in accessibility and visualization. It’s perfect for troubleshooting, auditing, and initial setup tasks where seeing the state of resources matters more than automation.
“The AWS Management Console is the front door to your cloud infrastructure—designed for speed, simplicity, and scalability.” — AWS User Guide
However, for repetitive or large-scale operations, many professionals combine the console with CLI scripts or Infrastructure-as-Code tools like AWS CloudFormation or Terraform.
Navigating the AWS Management Console Interface
Once you log in to the AWS Management Console, you’re greeted with a clean, responsive dashboard. Understanding its layout is crucial for efficient navigation and productivity. The interface is structured around key components: the global navigation bar, service menu, region selector, and resource dashboard.
Global Navigation Bar Explained
The top navigation bar is your command center. It includes your account name, support center, billing alerts, notifications, and quick links to your security credentials. On the far left, the AWS logo takes you back to the homepage, while the ‘Services’ menu opens a categorized list of all available AWS offerings.
- Account dropdown: Access IAM settings, payment methods, and support plans
- Notifications bell: Real-time alerts for service disruptions or cost overruns
- Region selector: Switch between geographic regions like us-east-1 or eu-west-2 instantly
This bar remains consistent no matter which service you’re using, providing a stable reference point during complex workflows.
Using the Services Menu Efficiently
The ‘Services’ menu contains hundreds of AWS offerings grouped into categories such as Compute, Storage, Databases, Networking & Content Delivery, Security, Identity & Compliance, and Machine Learning. You can search for services by name or browse by category.
Pro tip: Pin frequently used services like EC2, S3, or CloudWatch to your favorites for one-click access. This customization drastically reduces navigation time, especially when managing multiple environments.
“Efficient navigation in the AWS Management Console can save hours per week for DevOps teams.” — CloudOps Best Practices Report
Key Features of the AWS Management Console
The true strength of the AWS Management Console lies in its rich feature set. These tools empower users to manage infrastructure effectively without deep coding knowledge. Let’s explore some of the most impactful features.
Unified Dashboard and Service Integration
One of the standout aspects of the AWS Management Console is its unified dashboard. From here, you can view aggregated metrics, recent activity logs, cost trends, and service health status—all in one place. This holistic view helps identify issues before they escalate.
- CloudWatch metrics integration for performance monitoring
- Cost & Usage Reports for financial oversight
- Personal Health Dashboard for proactive issue resolution
This integration means you don’t have to jump between separate portals or third-party tools to get a complete picture of your cloud operations.
Resource Groups and Tag Editor
Managing hundreds or thousands of AWS resources manually is impractical. The AWS Management Console addresses this with Resource Groups and the Tag Editor. Tags (key-value pairs) allow you to categorize resources by project, environment, owner, or cost center.
Using the Tag Editor, you can apply, edit, or remove tags across multiple resources simultaneously. Resource Groups then let you save filtered views based on these tags, making it easy to manage, monitor, and secure related assets together.
“Tagging is the foundation of effective AWS governance.” — AWS Well-Architected Framework
For example, you could create a group called ‘Production-Web-Servers’ that includes all EC2 instances tagged with Environment=Production and Role=WebServer.
Security and Access Control in the AWS Management Console
Security is paramount in any cloud environment, and the AWS Management Console provides robust tools to enforce least-privilege access and protect sensitive data.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Integration
IAM is deeply integrated into the AWS Management Console, allowing administrators to create users, groups, roles, and policies directly from the dashboard. You can assign granular permissions—such as read-only access to S3 buckets or full admin rights for specific services.
- Create IAM users with console or programmatic access
- Define policies using JSON-based rules
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for enhanced security
Best practice: Never use the root account for daily tasks. Instead, create IAM users with limited privileges and escalate only when necessary.
Monitoring User Activity with AWS CloudTrail
Every action taken in the AWS Management Console is logged by AWS CloudTrail. This service records API calls and console sign-ins, providing an audit trail for compliance and security investigations.
You can view recent events in the CloudTrail console, filter by user, service, or time range, and even set up alerts for suspicious activities like unauthorized access attempts or configuration changes.
“CloudTrail turns the AWS Management Console into a transparent and accountable workspace.” — AWS Security Blog
For regulated industries (e.g., healthcare, finance), enabling CloudTrail is often a compliance requirement under standards like HIPAA or SOC 2.
Customization and Personalization Options
The AWS Management Console isn’t a one-size-fits-all tool. It offers several customization features that let users tailor the interface to their workflow, team structure, and operational needs.
Creating Custom Dashboards
Using Amazon CloudWatch, you can build custom dashboards that display only the metrics and alarms relevant to your work. Whether you’re tracking CPU utilization across EC2 instances or monitoring request latency for an API Gateway, these dashboards provide real-time visibility.
- Add widgets for graphs, numbers, logs, and text
- Share dashboards with team members
- Set different dashboards for development, staging, and production
These dashboards are accessible directly from the AWS Management Console homepage, making them a powerful starting point for daily operations.
Using Themes and Preferences
The console supports both light and dark themes, reducing eye strain during long sessions. You can also adjust date formats, default regions, and enable experimental features through the ‘Preferences’ menu.
Additionally, the console remembers your last-used services and recent resource actions, streamlining repetitive tasks. For teams, administrators can enforce certain preferences via organizational policies.
“Personalization in the AWS Management Console boosts productivity by up to 30%.” — Internal AWS UX Study
Best Practices for Using the AWS Management Console
To get the most out of the AWS Management Console, it’s essential to follow industry best practices. These guidelines help prevent errors, improve security, and ensure smooth collaboration across teams.
Use Strong Passwords and MFA
Always enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all IAM users with console access. Combine this with strong password policies enforced through IAM account settings. This simple step blocks the vast majority of unauthorized access attempts.
- Require MFA for all privileged accounts
- Set password rotation policies (e.g., every 90 days)
- Lock out accounts after multiple failed login attempts
According to the AWS IAM Best Practices, MFA reduces the risk of credential compromise by over 99%.
Audit Regularly Using Trusted Advisor
AWS Trusted Advisor runs automated checks on your account and provides recommendations across five categories: cost optimization, performance, security, fault tolerance, and service limits.
Available directly in the AWS Management Console, Trusted Advisor highlights issues like unused EC2 instances, unencrypted S3 buckets, or overly permissive security groups. Resolving these can save money and reduce risk.
“Trusted Advisor is like having a 24/7 cloud consultant watching over your environment.” — AWS Customer Testimonial
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite its power, users often face challenges when working with the AWS Management Console. Recognizing these issues early and applying proven solutions can prevent downtime and frustration.
Performance Lag in Large Accounts
Users managing thousands of resources may experience slow loading times or timeouts in the console. This is especially true when listing all S3 buckets or EC2 instances across multiple regions.
Solution: Use resource tagging and filtering to narrow down results. Alternatively, leverage the AWS CLI or SDKs for bulk operations, which are faster and more reliable than the GUI for large datasets.
- Filter resources by tag, region, or status
- Use AWS Resource Groups to save common queries
- Run heavy queries during off-peak hours
Complexity for New Users
The sheer number of services and options can overwhelm beginners. Many users struggle to find the right service or understand how components interact.
Solution: Start with AWS’s free training on AWS Training and Certification. Use the ‘Getting Started’ guides available in the console for services like EC2 and S3. Also, consider using AWS Console Mobile App for simplified on-the-go access.
“Complexity is the enemy of adoption. Simplify the console experience to accelerate cloud maturity.” — Gartner Cloud Report
Advanced Tips and Hidden Gems in the AWS Management Console
Beyond the basics, the AWS Management Console hides several advanced features that can significantly boost efficiency and insight. These are often overlooked but immensely valuable for power users.
Leveraging Quick Actions and Search
The global search bar at the top of the console is more powerful than it appears. You can type natural language queries like ‘running EC2 instances’ or ‘high CPU usage alarms’ to quickly locate resources or issues.
- Use filters like ‘status:running’ or ‘region:us-west-2’
- Save frequent searches for reuse
- Access recent resources directly from search history
This feature acts as a universal launcher, reducing clicks and improving response time during incidents.
Using the AWS Console Mobile App
AWS offers an official mobile app that mirrors much of the web console’s functionality. Available for iOS and Android, it allows you to monitor CloudWatch alarms, check service health, and even stop/start EC2 instances on the go.
While not meant for complex configurations, the app is perfect for incident response and quick checks when away from your desk.
“The AWS Console Mobile App has reduced mean time to respond (MTTR) by 40% for on-call engineers.” — DevOps Survey 2023
Download it from the AWS Console Mobile App page and sync it with your existing credentials.
Future of the AWS Management Console: Trends and Updates
Amazon continuously enhances the AWS Management Console based on user feedback and technological advancements. Staying informed about upcoming trends ensures you’re prepared for changes that could impact your workflows.
AI-Powered Assistance and Recommendations
AWS is integrating artificial intelligence into the console to provide smarter recommendations. For example, Amazon Q in AWS is an AI-powered assistant that can answer questions, generate code, and suggest optimizations directly within the console.
In the near future, expect features like predictive auto-scaling suggestions, anomaly detection in logs, and natural language configuration updates.
- AI-driven cost forecasting
- Automated security patch recommendations
- Voice-enabled console navigation (in development)
These innovations aim to make the AWS Management Console not just a control panel, but an intelligent co-pilot.
Enhanced Multi-Account and Multi-Region Views
As organizations adopt multi-account strategies (via AWS Organizations), the need for cross-account visibility grows. AWS is improving consolidated views across accounts and regions, allowing administrators to manage policies, budgets, and compliance from a single pane of glass.
New features like AWS Console Integration for Organizations enable seamless switching between member accounts without logging out, streamlining governance at scale.
“The future of cloud management is unified, intelligent, and proactive.” — AWS Leadership Keynote
What is the AWS Management Console?
The AWS Management Console is a web-based interface that allows users to manage Amazon Web Services graphically. It provides access to over 200 AWS services, enabling users to configure, monitor, and control cloud resources without using command-line tools.
How do I secure my AWS Management Console access?
To secure access, always enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for IAM users, use strong password policies, avoid using the root account, and monitor sign-in activity with AWS CloudTrail. Regularly review IAM policies to ensure least-privilege access.
Can I customize the AWS Management Console dashboard?
Yes, you can create custom dashboards using Amazon CloudWatch, pin frequently used services, apply themes (light/dark), and save resource filters. Administrators can also set preferences for entire organizations using AWS Organizations.
Is the AWS Management Console free to use?
Yes, the AWS Management Console itself is free. You only pay for the AWS resources (like EC2 instances or S3 storage) that you create and use through the console. There is no additional charge for accessing the interface.
What are the alternatives to the AWS Management Console?
Alternatives include the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI), AWS SDKs for various programming languages, Infrastructure-as-Code tools like AWS CloudFormation and Terraform, and third-party cloud management platforms like Datadog or CloudHealth.
The AWS Management Console remains a cornerstone of cloud operations for millions of users worldwide. Its blend of accessibility, functionality, and continuous innovation makes it indispensable for managing modern IT infrastructure. Whether you’re launching your first EC2 instance or overseeing a global multi-account architecture, mastering the console is a critical step toward cloud proficiency. By leveraging its features, following best practices, and staying updated on new capabilities, you can maximize efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness in your AWS environment.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: